C Gloassary j-s
long int : long int is a data type whose width is larger than or equal to int. Normally in 32 bit machines, a long integer is stored using 4 bytes and is similar to an int.
Synonym : long , signed long int, signed long
e.g.
Synonym : long , signed long int, signed long
e.g.
long int m = 4L;
long n;
printf("%d",sizeof(m));//prints 4
|
In line 1, the long literal is 4L which is used to specify the value is long integer. You must suffix long int literals with L or l.
long long int (C99): long long integer is normally 8 bytes integer. This type is available only in ANSI standard C99.
long double : This is a floating point data type which gives 19 digits precision and is stored using 10 or 12 bytes. The range of long double values are +-1.1E+4932. Remember that float gives 5 digits accuracy and double gives 15 digits accuracy.
#include <stdio.h> #include<float.h> #include <limits.h> int main() { printf("Size of long int is %d\n",sizeof(3L)); printf("The smallest long int is %ld\n and largest long int is %ld\n",LONG_MIN,LONG_MAX); long long int a; printf("Size of long long int is %d\n",sizeof(3LL)); printf("The smallest long long int is %lld\n and largest long int is %lld\n",LLONG_MIN,LLONG_MAX); long double b; printf("Size of long long double is %d\n",sizeof(b)); printf("The smallest long long int is %Le\n and largest long int is %Le\n",LDBL_MIN_EXP ,LDBL_MAX_EXP ); return 0; } |
Note:
- The limits.h and float.h header files are needed as they define the macros LONG_LONG_MIN and LONG_LONG_MAX.
- The macro LDBL_MAX_EXP defining long double max is giving erraneous answers in mingw gcc compiler and codepad provided online compiler.
#include <stdio.h> #include <limits.h> int main() { short int n=1; int i; printf("The range of short int is %hd to %hd and its width is %d\n",SHRT_MIN,SHRT_MAX,sizeof(n)); for(i=0;i<16;i++) { printf("2^%d is %hd\n",i,n); n = n<<1; } return 0; } |
The program prints the output as
The range of short int is -32768 to 32767 and its width is 2
2^0 is 1
2^1 is 2
2^2 is 4
2^3 is 8
2^4 is 16
2^5 is 32
2^6 is 64
2^7 is 128
2^8 is 256
2^9 is 512
2^10 is 1024
2^11 is 2048
2^12 is 4096
2^13 is 8192
2^14 is 16384
2^15 is -32768
The last value is negative because, the MSB is used as sign bit and if MSB is 1, the value is treated negative.

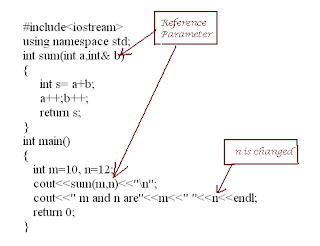
Comments
Post a Comment