Program to find lcm of first n numbers
I came across this problem in Project euler. http://projecteuler.net/problem=5
Find the smallest number which is divisible by all numbers from 1 to 20. 2520 is the smallest number which is divisible by all numbers from 1 to 10.
Now to find lcm of two numbers, we have a formula
lcm = product of a, b/ gcd of a,b
But lcm of more than two numbers? How do we calculate it?
lcm of a,b,c = lcm of ( lcm of a,b ) and c
lcm of a,b,c,d = lcm of (lcm of a,b,c) and d ... and so on.
To find gcd (greatest common divisor ) we have Euclid's algorithm
gcd(a,b) = b
if a is divisible by b i.e. a%b is 0
gcd (b, a%b)
if a is not divisible by b
So now we are almost ready to write our set of functions.
int gcd(int a,int b)
{
if ( a% b==0)
return b;
return gcd(b, a% b);
}
int lcm(int a,int b)
{
int product,hcf,divisor;
hcf = gcd(a,b);
if (hcf==b)
{
divisor = a;
}
else
{
divisor = (a*b)/hcf;
}
return divisor;
}
int lcm_first_n_numbers(int n)
{
int lc = 1; int i;
for( i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
lc = lcm(lc,i);
}
return lc;
}
As we can see, first function calculates gcd of two numbers, second function finds out lcm and third function calculates lcm of first n numbers iterativerly.
We added if (hcf==b)...... statement to avoid unnecessary multiplication and division if b is already gcd of a and b.
Things would run smoothly from here but for a problem. For larger numbers, lcm exceeds the integer range, we should use float instead. And % operator does not work on floats. So we should type cast the values to int.
Here are our functions with these changes
float gcd(float a,float b)
{
if (( int)a%( int)b==0)
return b;
return gcd(b,( int)a%( int)b);
}
float lcm(float a,float b)
{
float product,hcf,divisor;
hcf = gcd(a,b);
if (hcf==b)
{
divisor = a;
}
else
{
divisor = (a*b)/hcf;
}
return divisor;
}
float lcm_first_n_numbers(float n)
{
float lc = 1; int i;
for( i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
lc = lcm(lc,i);
}
return lc;
}
int main()
{
int n; float least_common_divisor;
printf("Enter n:");
scanf("%d",&n);
least_common_divisor = lcm_first_n_numbers(n);
printf("The smallest divisor of all numbers from 1 to %d is %f\n",n,least_common_divisor);
}
In fact I got wrong answer for n = 20, then I added the step of multiplying a and b only if gcd is not b. This gave me the correct answer. Problem was with floating point arithmetic.
Find the smallest number which is divisible by all numbers from 1 to 20. 2520 is the smallest number which is divisible by all numbers from 1 to 10.
Now to find lcm of two numbers, we have a formula
lcm = product of a, b/ gcd of a,b
But lcm of more than two numbers? How do we calculate it?
lcm of a,b,c = lcm of ( lcm of a,b ) and c
lcm of a,b,c,d = lcm of (lcm of a,b,c) and d ... and so on.
To find gcd (greatest common divisor ) we have Euclid's algorithm
gcd(a,b) = b
if a is divisible by b i.e. a%b is 0
gcd (b, a%b)
if a is not divisible by b
So now we are almost ready to write our set of functions.
int gcd(int a,int b)
{
if ( a% b==0)
return b;
return gcd(b, a% b);
}
int lcm(int a,int b)
{
int product,hcf,divisor;
hcf = gcd(a,b);
if (hcf==b)
{
divisor = a;
}
else
{
divisor = (a*b)/hcf;
}
return divisor;
}
int lcm_first_n_numbers(int n)
{
int lc = 1; int i;
for( i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
lc = lcm(lc,i);
}
return lc;
}
As we can see, first function calculates gcd of two numbers, second function finds out lcm and third function calculates lcm of first n numbers iterativerly.
We added if (hcf==b)...... statement to avoid unnecessary multiplication and division if b is already gcd of a and b.
Things would run smoothly from here but for a problem. For larger numbers, lcm exceeds the integer range, we should use float instead. And % operator does not work on floats. So we should type cast the values to int.
Here are our functions with these changes
float gcd(float a,float b)
{
if (( int)a%( int)b==0)
return b;
return gcd(b,( int)a%( int)b);
}
float lcm(float a,float b)
{
float product,hcf,divisor;
hcf = gcd(a,b);
if (hcf==b)
{
divisor = a;
}
else
{
divisor = (a*b)/hcf;
}
return divisor;
}
float lcm_first_n_numbers(float n)
{
float lc = 1; int i;
for( i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
lc = lcm(lc,i);
}
return lc;
}
int main()
{
int n; float least_common_divisor;
printf("Enter n:");
scanf("%d",&n);
least_common_divisor = lcm_first_n_numbers(n);
printf("The smallest divisor of all numbers from 1 to %d is %f\n",n,least_common_divisor);
}
In fact I got wrong answer for n = 20, then I added the step of multiplying a and b only if gcd is not b. This gave me the correct answer. Problem was with floating point arithmetic.

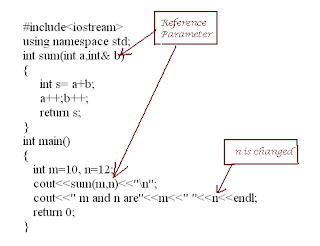
Great and Simple Programs. Would also recommend your readers to have a look at C Program To Find LCM of N Numbers using Functions and Arrays. It is described in two different scenarious.
ReplyDelete