Static members in C++
Static data member
A static data member belongs
to the class, not to any object. It is shared by all the objects of the
class.
To make a data member static,
it should be defined with keyword static inside the class body.
A static data MUST also be defined outside
the body of the class because inside class, the declaration of static
data is not definition.
class SimpleInterest { static double rate; int amount; float period; public: /*funnctions*/ }; double SimpleInterest::rate=0.07;/*definition*/
Static data members can be
accessed using dot or arrow operator but they can also be accessed without an object,
using class name followed by scope resolution operator.
int main() { SimpleInterest::rate=0.08; SimpleInterest obj; float intrst = obj.amount*obj.period*obj.rate; cout<<intrst; }
Static member functions
A static member function can
be called directly without using any object, with class name and
scope resolution operator.
A function is made static by
using static keyword within the class body in function declaration.
Rules for static functions.
- A static function can not use "this" pointer. Hence it can not access non-static data members.
- A static function can not be const
- Static function can not be virtual
class A { int n; static int m; public: A(int m); static void print() ;/*static function*/ }; int A::m=4; void A::print() { cout<<"Hello world"; cout<<n;/*error. Can not access n*/ cout<<m;/*no error. m is static*/} int main() { A::print(); }
print() function of A class, which is
static can not access n, as n is non-static data.

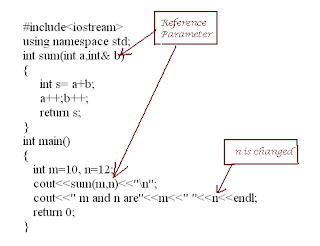
Comments
Post a Comment